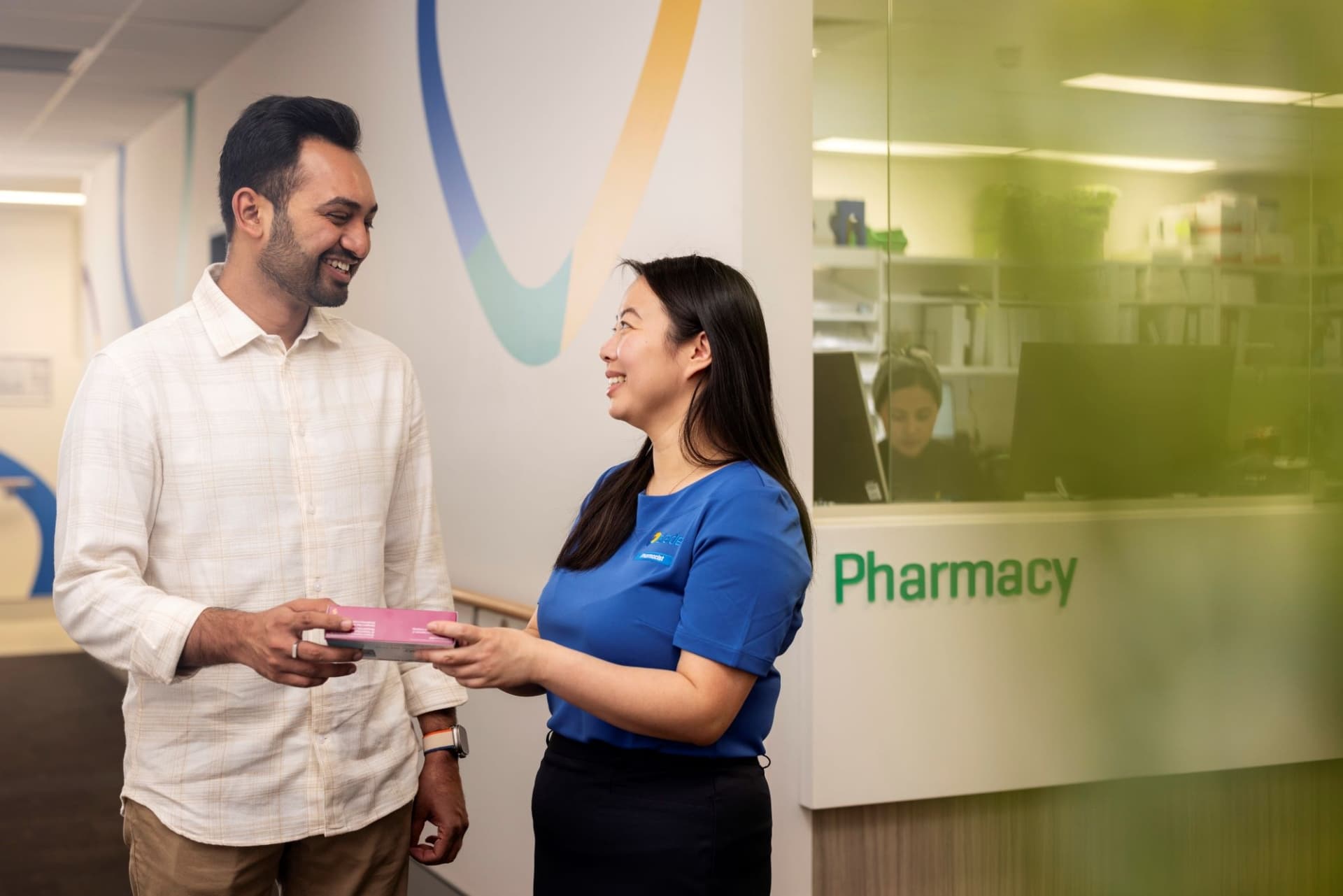
Antibiotics are usually prescribed for treating a possible or known infection.
Before you are prescribed antibiotics, blood tests, urine samples or wound swabs may be taken to try to work out which antibiotic is the best to treat the infection. The results of these tests may lead to your antibiotic treatment changing or stopping.
It is important to take the antibiotics for the period of time advised by your doctor to treat your particular infection, which may be different to the size of the packet.
Advise your doctor, nurse or pharmacist about any allergies to medications you have had in the past. If you are taking an antibiotic and experience a rash, swelling of the throat/mouth, or other side effects, tell your doctor or nurse promptly.
If you are receiving antibiotic injections and you are eating and drinking without any restrictions, ask your doctor if it is possible to switch to oral antibiotics (e.g. tablets or capsules).
Sometimes antibiotics will be used to prevent an infection. If you are having a medical procedure that could increase your risk of infection, an antibiotic may be recommended before, during or shortly after the procedure, as per recommended guidelines. Your doctor may also recommend antibiotics if your immune system is too weak to fight off a serious infection.